The Beijing Metropolitan Area (BMA) covers an area of 16,410 km2 and has a population of more than 22 million as of 2015. It is the anchor city of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei polycentric urban region. The master plan of BMA has envisioned a intra-urban polycentric structure with one central city and a number of ‘edge cities’.
Beijing’s public transport system consists of buses and subways. According to Beijing Transportation Research Center, the share of public transport trips was 38.9% in Beijing, making it the largest public transit system regarding daily ridership in China. While bus riders account for 29% of the daily ridership, 95% of bus users are smart card holders in Beijing.
For this project, we were granted access to two sample data:
- A full week’s historical data containing 77,976,010 bus trips of 8,549,072 anonymized cardholders between 4/7/2008 and 4/13/2008.
- A four-day (4/6/2010–4/10/2010) weekday public transit smartcard records of student riders, including a total number of 158,262 trips.
For Bus Commuters
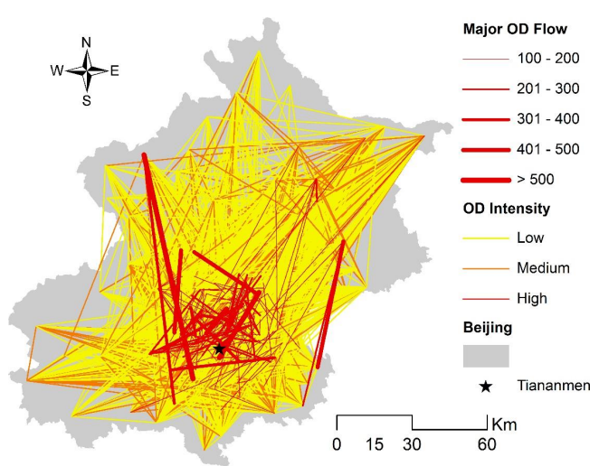
Origin-destination flows for bus commuters between residence and employment locations:
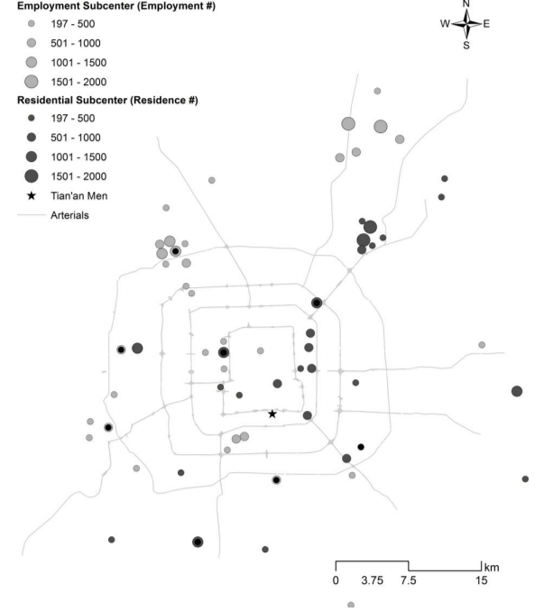
Employment and residential (sub)centers of bus commuters:
For College Students
- ‘985 universities‘: A shortlist of top universities designated by the Chinese Central Government in 1999.
Top student transit trip destinations
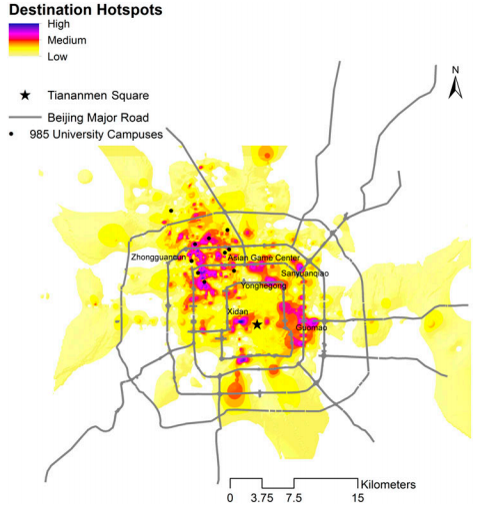
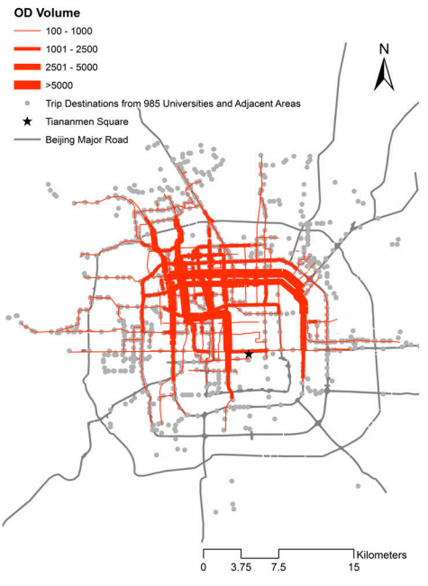
Distribution of all transit trips from the campuses.
References
- Mingshu Wang, Jiangping Zhou, Ying Long, Feng Chen (2016).Outside the ivory tower: visualizing university students’ top transit-trip destinations and popular corridors. Regional Studies, Regional Science, 3(1), 202-206.
- Jiangping Zhou, Mingshu Wang, Ying Long (2017). Big data for intrametropolitan human movement studies: A case study of bus commuters based on smart card data. International Review for Spatial Planning and Sustainable Development, 5(3), 100-115 (Corresponding Author).